Third-Party Risk Assessment Best Practices

Properly assessing the potential hazards posed by third parties is a crucial element of an organization's risk management strategy. Third-party risks can include cybersecurity threats, data privacy concerns, compliance issues and operational risks – as well as environmental, social, and governance (ESG) risks, financial risks and reputational risks. By conducting thorough third-party risk assessments tailored to a specific risk profile, your organization can identify and mitigate unacceptable risks throughout the lifecycle of its vendor and supplier relationships.
Third-party risk assessments not only enable your organization to proactively detect and reduce risks, but also help it prepare for potential incidents. Furthermore, conducting comprehensive third-party risk assessments builds trust with customers, provides additional evidence of compliance to regulatory bodies, and empowers your organization to uncover and understand risk throughout its distributed supply chain.
What Is a Third-Party Risk Assessment?
Third-party risk assessments are conducted throughout the vendor risk lifecycle to holistically assess the organizational risk posed by specific vendors and suppliers. Organizations typically conduct assessments at several points during the third-party relationship, including:
During the initial selection and sourcing phase to identify and prioritize potential suppliers and vendors with acceptable risk profiles
Before granting access to sensitive systems and data during the onboarding process, as a form of due diligence to evaluate potential hazards
Periodically throughout the partnership in order to verify compliance with service level agreements, evaluate adherence to contracts, and fulfill audit requirements
During the offboarding process, to ensure that system access is terminated and data is protected or disposed of in accordance with regulations
In the event of a security incident to determine the scope and impact of the breach
Third-party risk assessments leverage questionnaires that solicit information about a third party's security and privacy controls. They may also gather information about the third party's financial and operational data, as well as their policies on environmental, social and governance (ESG) issues. The risks identified during the assessment process are generally evaluated based on factors such as severity of the issue and likelihood of occurrence. The results are often mapped to key requirements outlined in industry or regulatory frameworks such as ISO, HIPAA, PCI DSS, UK Modern Slavery ACT, GDPR, NIST CSF and other core regulations. This helps organizations take a proactive approach to identifying and mitigating risks associated with working with external partners.
Third-Party Risk Assessment Explained
Watch this video to learn how assessments enable you to not only proactively identify and mitigate third-party risks, but also be better prepared for when vendor and supplier incidents do occur.
Why Are Third-Party Risk Assessments Essential?
In recent years, global business and supply chains have been severely disrupted by events such as the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, extreme weather, significant cyberattacks, and other crises. These disruptions have led to operational failures, financial losses, and legal challenges for many organizations. Although many of these events were unavoidable, organizations with strong third-party risk management (TPRM) programs were often able to minimize or mitigate their effects.
By implementing a robust third-party risk assessment process, your organization can deepen its understanding of its third-party supply chain and holistically assess hard-to-find risks such as concentration risk, fourth-party ESG risk, and reputational risk. This strengthens its resilience during crises while enabling it to make intelligent, informed business decisions about the risk posed by engaging new vendors.
What Are The Different Categories of Third-Party Risk?
When working with third parties, there are three main types of risks to consider: profiled, inherent, and residual. These risk types inform the level of depth your assessment process should take and the remediation actions you should require from vendors based on their information security and business practices.
Profiled Risk is the risk a third party poses to your organization based on externally observable information such as their location, industry, usage of fourth parties, ownership, or basic ESG policies. Third parties with operations in a geopolitically unstable region or one that leverages several third parties of its own may deserve additional scrutiny during the third-party risk assessment process.
Inherent Risk is the risk that a third party poses based on their internal controls and business practices. For example, an organization that will access your customer data and has been third-party audited and verified to comply with GDPR may have a lower inherent risk score than an organization without a formalized information security or data privacy program.
Residual Risk is the level of risk that remains after the vendor has implemented your organization's requirements or if they have implemented the appropriate compensating controls. Residual risk is sometimes called "acceptable risk" when an organization accepts the remaining risks associated with the third party.
It's important to consider these three types of risks when assessing and managing third parties to effectively identify, mitigate, and manage the potential hazards they may pose to your organization.
How Do You Score Third-Party Risks?
Assessing third-party risk involves calculating risk scores that account for the likelihood of an event occurring and its potential impact. For instance, consider a vendor that provides services to a hospital and handles large amounts of protected health information (PHI) but is not compliant with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
In this case, the vendor would be classified as a business associate and subject to the same regulatory requirements as the healthcare provider. The impact in this scenario would be significant, potentially resulting in fines for both the healthcare provider and the business associate. The likelihood of regulators discovering non-compliance would also be high. This would represent an unacceptable risk for any healthcare organization and would likely result in the termination of the contract.
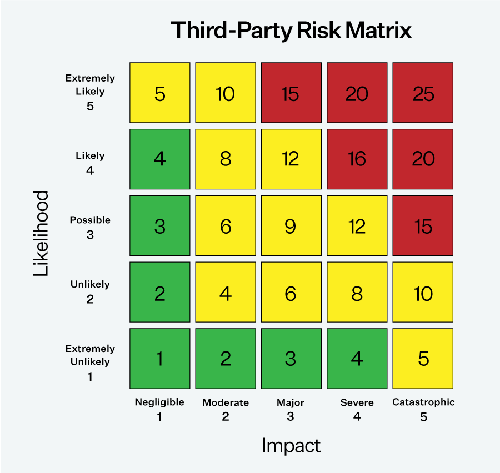
This example emphasizes the significance of conducting extensive third-party risk assessments, particularly for organizations that handle large amounts of sensitive data, such as government contractors and healthcare providers. In many situations, regulations like HIPAA hold the primary organization accountable for non-compliance by their vendors, making it crucial for organizations to properly evaluate and mitigate the risks associated with their third-party relationships.
Third-Party Risk Assessment Steps
1. Assemble Internal Stakeholders
The most successful third-party risk assessment programs involve stakeholders' input and/or participation, representing multiple roles with different priorities. Understanding these priorities can help streamline your program and ensure that key steps aren’t missed or overlooked. By assembling a cross-functional team to plan and guide your assessment program, you can help to ensure organizational adoption and long-term success.
2. Define Your Acceptable Level of Residual Risk
It is important to understand that even with the best efforts, some level of risk will always be present when working with third parties. Before assessing potential partners, you need to establish what level of risk is acceptable for your organization. This will help make vendor selection and risk management more efficient and uniform. This method can also help you quickly identify third parties that may not align with your business objectives and risk tolerance.
3. Build Your Third-Party Risk Assessment Process
To effectively manage third-party risk, it is essential to have a standardized process in place. However, the risk assessment process may vary depending on the third party, their level of criticality to your supply chain, access to sensitive data, and susceptibility to continuity events. For example, third parties with high criticality and potential risk will require more thorough due diligence than those with lower risk. A structured process will enable your program to operate more efficiently and help you make better, risk-based decisions about your third-party relationships.
Starting with an internal profiling and tiering assessment can help categorize your vendors and map out the type, scope, and frequency of assessment required for each group.
4. Send Third-Party Risk Assessment Questionnaires
To effectively manage third-party risk, gathering information about the vendor's internal controls is important. One way to do this is by sending out questionnaires. These questionnaires can cover a wide range of topics, such as information security practices, compliance requirements, financial stability, and fourth—and Nth-party supplier data.
When choosing questionnaires for primary risk assessments, companies must decide whether to use an industry-standard questionnaire or create their own. Standardized questionnaires like the Standard Information Gathering (SIG) questionnaire, the H-ISAC questionnaire for healthcare organizations, and the Prevalent Compliance Framework (PCF) questionnaire are widely accepted and familiar to most vendors and suppliers. However, if a third party already has an information security certification, such as CMMC or SOC 2, it may be accepted in lieu of requiring an assessment response. Alternatively, you may supplement them with proprietary and/or ad-hoc assessments to gather information about specific controls or potential risks outside of cybersecurity.
Another option is to use frameworks when designing vendor assessment questionnaires. Frameworks like the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, ISO 27001, and NIST 800-30 can help ensure that questionnaires are standard across the supply chain and reflect best practices. Additionally, if specific regulations like the GDPR or PCI-DSS apply, it may be beneficial to incorporate questions related to those standards directly into the program.
Free Template: Top 20 TPRM Questions (XLS)
Use this free third-party risk questionnaire to jump start your third-party risk assessment process with the top 20 control questions to ask vendors.

5. Complement Assessments with Continuous Risk Monitoring
Cybersecurity vulnerabilities, supply chain challenges, and compliance requirements evolve continually. Therefore, conduct continuous risk monitoring to catch any cyber, business, financial, or reputational risks arising between your periodic vendor assessments. You can also use risk data to verify that a third party's assessment responses are consistent with real-world business activities.
Vendor Data Breaches, Exposed Credentials, and Other Cyber Risks
In today's constantly evolving cyber landscape, organizations must proactively monitor external cybersecurity risks across their vendor ecosystem rather than take a one-off approach to assessing vendor risk. Potential risks to keep an eye out for include:
Credential exposures
Confirmed data breaches and incidents
Misconfigured web applications and vulnerabilities
Typosquatting and other brand threats.
For more information on identifying these and other risks, refer to our post on Cyber Supply Chain Risk Management (C-SCRM) Best Practices.
Third-Party Finances, Business Practices, and Reputation
In addition to cybersecurity risks, monitoring suppliers' financial stability, business practices, and reputation is crucial. Financial failure, operational disruptions, or negative press can have significant implications for your business and environmental, social, and governance (ESG) challenges, such as modern slavery, bribery/corruption, and consumer protection issues. To mitigate these risks, research suppliers' business practices, raw material sourcing, and other key processes that could pose reputational or ethical concerns. Additionally, request reference customers and partners to gain further insight into the third party's ability to meet SLAs and other contractual obligations.
Selecting a Monitoring Strategy
It's important to have a comprehensive and efficient strategy when building a monitoring program. Many companies leverage automated vendor threat monitoring software for risk identification and scoring. This can help organizations efficiently gather intelligence from various sources, such as open-source intelligence.
6. Categorize and Remediate Risks
When assessing third-party risks, it's essential to categorize them as either acceptable or unacceptable. Unacceptable risks must be addressed before working with the vendor. Remediating these risks can take various forms, such as requiring a security certification like SOC 2, ending relationships with fourth—and Nth-party vendors, or changing business practices that could lead to supply chain or other disruptions.
Having a defined incident response strategy is also crucial in a data breach or other disruption caused by a vendor. With a pre-established plan, you can significantly speed response time and minimize the impact on your organization.
How to Start a Third-Party Risk Assessment Program
Many companies make the mistake of using a combination of email and spreadsheets when launching an assessment program. This manual approach can be time-consuming and challenging to manage, especially when working with many vendors. It also often results in limited and unreliable data.
To create an effective assessment program, consider using a vendor intelligence network that provides access to a library of vendor risk reports based on standardized assessment data. Another option is an automated third-party risk assessment solution, allowing for greater customization and control over the assessment process. Alternatively, a managed service provider can conduct assessments on your behalf if a more hands-off approach is preferred.
Next Steps
Prevalent offers third-party risk assessment solutions and services as part of our comprehensive third-party risk management platform. To discuss your specific needs with a Prevalent expert, request a personalized demo today.
-

The Top 7 TPRM Predictions for 2025
2025 promises to be a consequential year for third-party risk management. Read our top TPRM predictions...
12/12/2024
-

Developing a Third-Party Risk Management Policy: Best Practice Guide
Learn how a third-party risk management (TPRM) policy can protect your organization from vendor-related risks.
11/08/2024
-

Vendor Offboarding: A Checklist for Reducing Risk and Simplifying the...
Follow these 7 steps for more secure and efficient offboarding when third-party relationships are terminated.
10/17/2024
-
Ready for a demo?
- Schedule a free personalized solution demonstration to see if Prevalent is a fit for you.
- Request a Demo




