MAS Outsourcing Guidelines and Third-Party Risk Management

Founded in 1970, the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) is a central bank and financial regulator that provides prudential oversight of all financial institutions in Singapore – including ensuring financial and operational resilience against risks. In July 2016, MAS delivered guidelines on outsourcing third-party arrangements. MAS expanded their outsourcing guidance in October 2018, and again in August 2022 with the publication of an information paper, Operational Risk Management – Management of Outsourcing and Third Party Arrangements. In the information paper, MAS:
- Published detailed requirements on how to achieve better oversight and governance over third parties; and
- Established comprehensive guidance on conducting due diligence over the lifecycle of outsourcing arrangements.
The figure below identifies the types of approvals required, assessments, assessment frequencies, and due diligence documentation that should be provided to support assessments as explained in the Management of Outsourcing and Third Party Arrangements information paper.
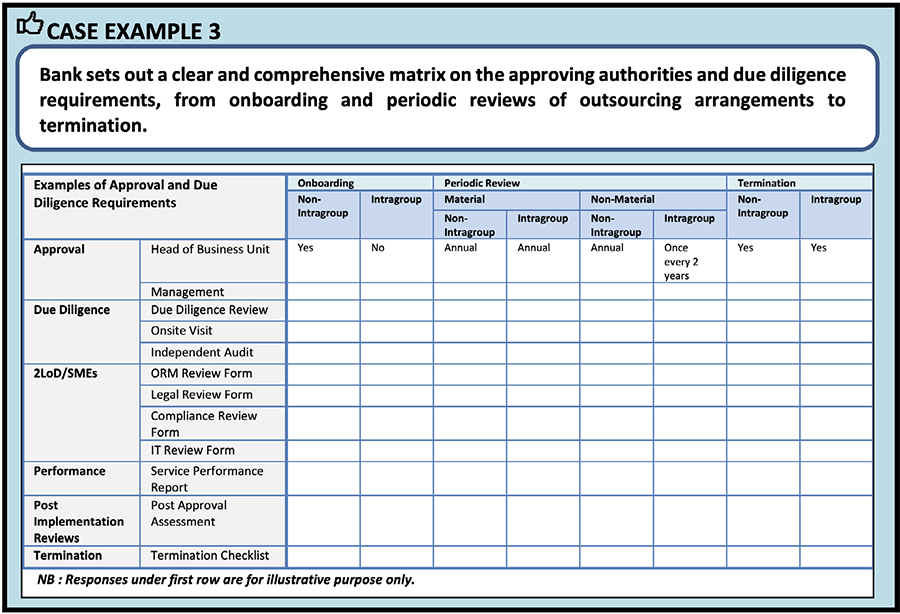
Courtesy: Operational Risk Management – Management of Outsourcing and Third Party Arrangements – Observations and Supervisory Expectations from Thematic Inspections – Information Paper, August 2022
This post examines key MAS provisions that govern outsourcing and non-outsourcing arrangements, and identifies best practices capabilities that can be used to address MAS requirements.
MAS Outsourcing and Non-Outsourcing Guidelines
The MAS Operational Risk Management – Management of Outsourcing and Third Party Arrangements information paper, chapter 3, includes specific guidance for financial institutions in the following general areas of the third-party risk management lifecycle:
- Governance and management oversight
- Identification and risk categorization
- Due diligence (including onboarding and periodic reviews)
- Ongoing risk management and monitoring
Governance and Management Oversight
MAS requires financial services organizations to establish a governance structure and framework; set risk appetites; and establish management reporting.
To address these requirements, financial services organizations should consider defining the following criteria as part of their third-party risk management program:
- Governing policies, standards, systems and processes to protect data
- Clear roles and responsibilities (e.g., RACI) for all members of the team
- Risk scoring and thresholds based on your organization’s risk tolerance
- Assessment and monitoring methodologies based on third-party criticality
- Fourth-party mapping to determine upstream dependencies
- Sources of continuous monitoring data (e.g., cyber, business, reputational, financial) to provide constant insight into emerging risks
- Contractual key performance indicators (KPIs) and key risk indicators (KRIs) to measure against
- Incident response requirements to prepare for potential disruptions
- Reporting to meet the needs of multiple internal (and external) stakeholders
- Risk mitigation and remediation strategies, including the applicability of compensating controls
Many organizations choose to align with an accepted risk management framework, such as ISO, to accomplish this. If you are looking to automate the process of measuring your TPRM program against an industry framework, be sure to select an assessment platform that provides several pre-built questionnaire options that align with multiple frameworks.
The MAS Third-Party Compliance Checklist
Download the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) Third-Party Compliance Checklist to identify key MAS provisions that govern outsourcing and non-outsourcing arrangements.

Identification and Risk Categorization
MAS requires organizations to identify and categorize third-party dependencies. This includes establishing a management and governance framework; identifying and inventorying third parties; categorizing them based on their nature and risk characteristics; and establishing criteria to determine the governance and due diligence requirements that they should be subject to.
To address these requirements, financial institutions should:
- Build a comprehensive vendor profile that includes demographic information, ownership, financial performance, CPI scores, Modern Slavery statements, industry and business insights, and maps potentially risky 4th-party relationships. This helps centralize third party information, providing a single source of the truth for vendor management across their relationship lifecycle.
- Perform inherent risk assessments on their third parties in order to tier them; set appropriate levels of further diligence; and determine the scope of ongoing assessments for all third parties. Criteria can include:
- Criticality to business performance and operations
- Location(s) and related legal or regulatory considerations
- Level of reliance on fourth parties (to avoid concentration risk)
- Exposure to operational or client-facing processes
Due Diligence (Onboarding and Periodic Review)
In terms of due diligence and performing periodic reviews, MAS recommends taking the results generated from the identification and risk categorization exercise and developing an onboarding plan that facilitates ongoing reviews.
Third-party risk assessments should be conducted at the beginning of a relationship to gain a picture of the risks the third party presents to your organization; at the time of contract renewal; and whenever there is a compelling event such as a breach, compliance violation or other failure. Critical success factors include having access to a large library of questionnaire templates to add flexibility to assessment efforts, and prescriptive remediation recommendations to hold third parties to account. As part of this process, be sure to:
- Review third-party assessment responses and documentation against established testing protocols to validate that indicated controls are in place.
- Map the responses to your organization’s selected control framework.
- Develop remediation plans and track them to completion.
Ongoing Risk Management and Monitoring
To enable ongoing risk management, MAS recommends deploying adequate risk monitoring tools and mechanisms to manage third party risk. Monitor the Internet and dark web for cyber threats and vulnerabilities, as well as public and private sources of reputational, sanctions and financial information.
All monitoring data should be correlated to assessment results and centralized in a unified risk register for each third party, streamlining risk review, reporting and response initiatives. Risks can be categorized into a heat map view with likelihood and impact axes.
Monitoring sources should include a mix of cyber and non-cyber sources to gain a comprehensive picture of a third party’s risk. Examples include:
- Cyber: Criminal forums; onion pages; Dark Web special access forums; threat feeds; paste sites for leaked credentials; security communities; code repositories; vulnerability databases; and data breach databases
- Business: M&A activity; business news; and operational updates
- Reputation: Negative news; and politically exposed persons (PEPs).
- Regulatory and legal: Global sanctions lists; and global enforcement lists and court filings
- Financial: Financial performance; credit scores; shareholder funds; beneficial ownership.
How Prevalent Helps Address MAS Third-Party Risk Management Requirements
The Prevalent Third-Party Risk Management Platform automates workflows required to onboard, periodically review and terminate material and non-material third-party outsourcing arrangements, delivering key capabilities for multiple teams to centralize TPRM across the enterprise. The solution delivers specific capabilities that address all due diligence requirements, from approval to termination.
Prevalent helps financial organizations add governance and oversight to their outsourcing and non-outsourcing arrangements by:
- Building a comprehensive, agile and mature third-party risk management program based on proven financial industry best practices
- Centralizing third-party profiles for a single enterprise-wide inventory of outsourcing and non-outsourcing arrangements
- Automating the identification and assessment of critical third parties based on their criticality to the organization
- Assessing and continuously monitoring for cybersecurity, business, financial and reputational risks
- Measuring against key performance indicators (KPIs) and key risk indicators (KRIs)
- Delivering remediation recommendations to reduce third-party residual risk
- Including templates to simplify regulatory and security framework audit reporting to multiple internal and external stakeholders
For more on how Prevalent can help address the requirements in MAS Operational Risk Management – Management of Outsourcing and Third-Party Arrangements, download our complete MAS checklist or request a demo today.
-

Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA): How to Assess Third-Party Anti-Bribery...
On February 10, 2025, the Trump Administration announced a pause in FCPA enforcement actions while a...
02/11/2025
-

How to Meet EBA Guidelines for Managing Third-Party ESG Risks
The new EBA Guidelines require financial institutions to assess, monitor, and manage ESG risks in their...
01/22/2025
-

SIG 2025: Key Updates and Considerations
Uncover key changes in the Standard Information Gathering (SIG) Questionnaire for 2025 and learn what these...
12/16/2024
-
Ready for a demo?
- Schedule a free personalized solution demonstration to see if Prevalent is a fit for you.
- Request a Demo




